
Name: Vanessa Awando
Class: SL Biology C
Date: 22/02/2016
Page Title
Porifera
KINGDOM ANIMALIA

Animals are eukaryotic, multicellular and heterotrophic (An organism that cannot make it’s own food instead it obtains it’s food and energy from organic substances). This Kingdom is the most diverse as it contains organisms/animals of a wide variety. Below we will be looking at 7 different phyla which are used to further categorize organisms found in the Animalia Kingdom.
Phylum Porifera (Sponges): This phylum contains sponges which are marine animals. Sponges are known to be sessile (non moving). Sponges contain no muscle or nerve tissue and they have no distinct internal organs such as a heart. They have perforated (hole/pierced) bodies made up of two layers of cells. Water is pumped the body wall to the animal, this is where food in the water is trapped and taken in by the sponge. This is due to the fact that they have no mouth or digestive tracts. They have no clear symmetry,
Phylum Cnidaria (Jellyfish, Corals): This phylum includes corals, sea anemones, jellyfish, hydra. These animals all have stinging cells called nematocysts. Some are sessile others are mobile and some can be both. These animals digest their food by grasping it with their tentacles. They contain a gastric pouch with a single opening. They are radially symmetrical.
Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms): Animals in this phylum are both parasitic and nonparasitic examples of these include planaria, tapeworms and flukes. These animals have one body cavity this includes an opening for food to enter and waste products to exit. Their bodies are not segmented and they do not have any lungs or hearts. Flatworms are flat because all cells in the body need to be close to the body so that gases can be exchanged through diffusion. They are bilaterally symmetrical.
Phylum Annelida (Segmented worms): In this phylum segmented worms are found these include leeches, polychaetes and earthworms. These animals have bodies which are divided by rings around their body. They contain a gastric tract with a mouth at one end and an opening at the other so that waste can be released. Contain bilateral symmetry.
Phylum Mollusca: This phylum contains animals such as slugs, snails and octopus. Bodies of these animals are not segmented, they produce a shell which contains calcium and a one way digestive system where the mouth and anus are located.
Phylum Arthropoda: Animals such as insects, spiders millipedes,crabs and shrimps and butterflies. These animals contain a hard exoskeleton that is made of chitin. They have joined body segments and jointed limbs to each segment which allows them to bend and be mobile. They are bilaterally symmetrical.
Chordata Phylum: This phylum contains animals with a backbone they are also known as vertebrates. Animals in this phylum have notochord (a cartilaginous skeletal rod supporting the body) at some point during their development. examples of these include birds, mammals. amphibians, reptiles (turtles) and fish. They have bilateral symmetry.
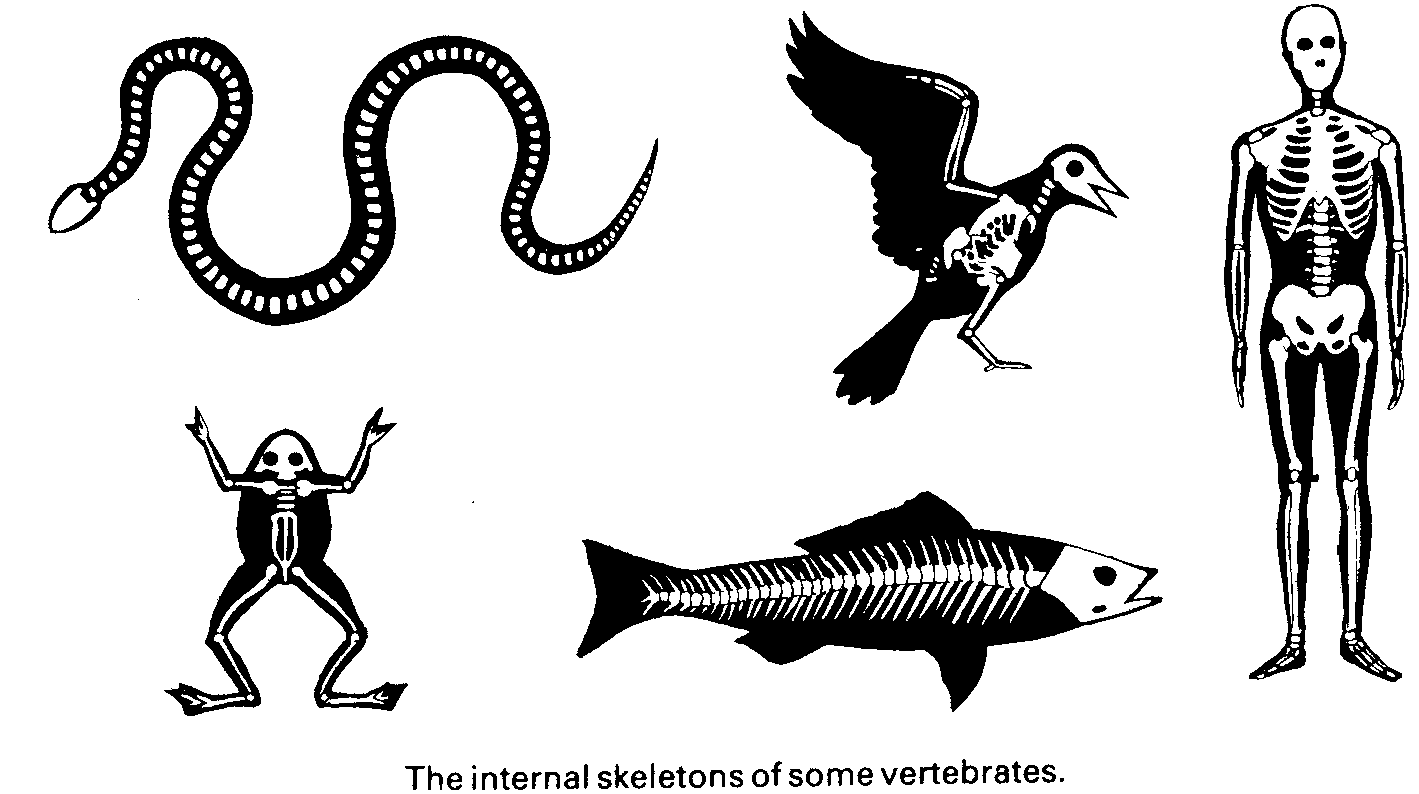
Chordata
Mollusca
"Animal Classification." Animal Classification. 2008. Web. 20 Mar. 2016. <http://a-z-animals.com/reference/animal-classification/>.
Wright, Judene. Cracking the SAT Biology E/M Subject Test. 2011 - 2012 ed. New York: Princeton Review, 2011. Print. Biology.

Cnidaria

Anthroproda

Platyhelminthes

Annelida
